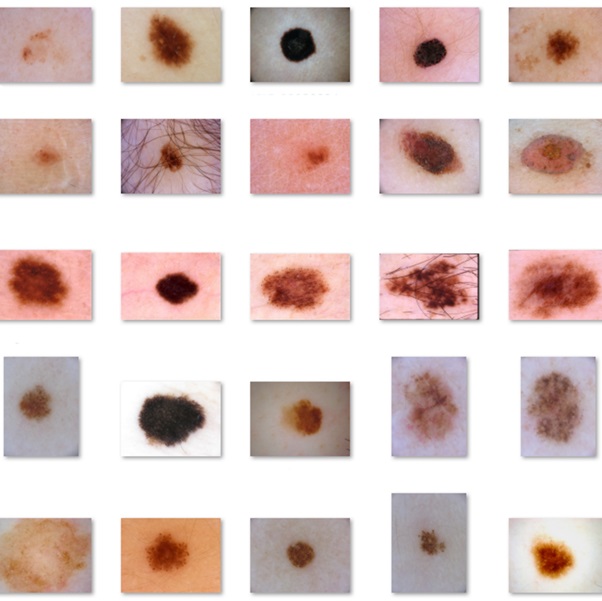
The use of image processing for skin disease detection is a rapidly developing field with the potential to revolutionize healthcare. It offers a non-invasive, potentially low-cost alternative to traditional diagnostic methods, often with faster results.
Here’s an overview of how it works:
- Image Acquisition: The process begins with taking a picture of the affected skin area using a camera or smartphone.
- Preprocessing: The image is then preprocessed to enhance relevant features and remove noise. This might involve tasks like:
- Color Space Conversion: Converting the image to a grayscale or specific color space (e.g., HSV) to highlight specific characteristics.Noise Removal: Applying filters to remove noise and artifacts that could interfere with analysis.
- Segmentation: Isolating the lesion from the surrounding healthy skin for focused analysis.
- Feature Extraction: After preprocessing, relevant features are extracted from the image. These features could include:
- Color and Texture: Analyzing color variations, patterns, and textures within the lesion.Shape and Size: Measuring the lesion’s dimensions and comparing them to known disease characteristics.
- Border Properties: Analyzing the edges of the lesion for regularity, smoothness, or other distinguishing features.
- Classification: Extracted features are then fed into a machine learning model or other classification algorithm. These algorithms compare the features to a database of known skin diseases and predict the most likely diagnosis.
- Result and Recommendation: The algorithm outputs a potential diagnosis or a list of likely possibilities. This information is then reviewed by a medical professional for final diagnosis and treatment planning.
Technologies used in skin disease detection:
- Machine Learning: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are particularly effective due to their ability to learn complex patterns from image data.
- Image Processing Techniques: Thresholding, edge detection, color segmentation, and texture analysis are commonly used pre-processing and feature extraction techniques.
- Computer Vision: Techniques like lesion tracking and image registration can be used to monitor disease progression over time.
Benefits of image processing for skin disease detection:
- Early detection: Can catch diseases in their early stages, leading to better treatment outcomes.
- Accessibility: Can be used in remote areas or for self-screening, improving access to healthcare.
- Cost-effectiveness: This can be a more affordable alternative to traditional diagnostic methods.
- Non-invasive: Avoids the need for biopsies or other invasive procedures.
Challenges and limitations:
- Accuracy: Requires large datasets for training algorithms and can be susceptible to factors like lighting and image quality.
- Limited scope: Not all skin diseases have distinct visual features, and some require additional tests for confirmation.
- Professional interpretation: Final diagnosis and treatment still require a medical professional’s expertise.