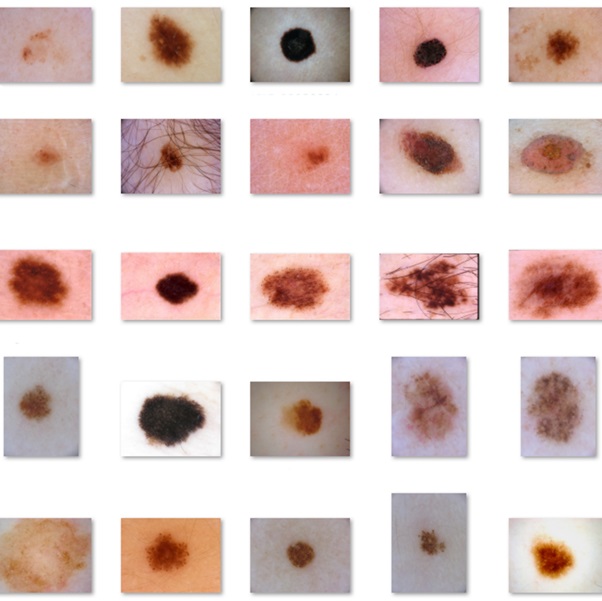
Protein fibrillation, which has caused a number of diseases and is a hindrance to the biopharmaceutics and protein industries, has emerged as one of the significant issues in the biomedical sector over the past few decades. Numerous substances, including flavonoids, surfactants, nanoparticles, and micelles, have been widely used as hopeful therapeutic agents to treat amyloidogenic disorders like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, type 2 diabetes, etc. Membrane disruption, organ malfunction, and apoptosis are all caused by the oxidative damage that fibrillar aggregate deposition causes to cellular membranes. Therefore, it is essential to discover new substances that can block the process of protein fibrillation. Here, our main goal is to create brand-new therapeutics that could revolutionise the way we treat neurodegenerative diseases caused by aggregation. We believe that a thorough understanding of the way in which therapeutic medicines interact with amyloid aggregates at various phases of fibrillation will contribute to a better understanding of the aggregation process’s mechanism. This can be used as a powerful design tool to create brand-new inhibitors that are powerful enough to effectively treat neurodegenerative conditions and advance our understanding of protein aggregation. Our another major research interest is in the field of nanomaterials & drug delivery. The low water solubility and poor bioavailability of certain phenolic chemicals, such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and their metal complexes, limits their use in the biomedical area. The stability and bioavailability of these substances will be improved by encapsulating them in protein- and polymer-based nanoparticulate systems. The creation of innovative nano-formulations is anticipated to offer an efficient means of delivering flavonoids and flavonoid-metal complexes to the desired target site and enhancing their antibacterial and anticancer capabilities. This type of delivery technology benefits from efficient encapsulation, controlled release, precise targeting, and biodegradable characteristics. It will be possible to learn more about medication distribution by seeing how synthesized nano-formulations interact with lipids, nucleic acids, or serum albumins.